Introduction
Marking is the process of transferring a design or pattern to a workpiece and the tool used for marking is known as a marking tool. During manufacturing processes, there must be some guidelines that help to achieve the desired shape of the workpiece. The most important step in manufacturing is marking or layout of guidelines on the workpiece before the machining or cutting operation.
Purposes of Marking Media
The purpose of marking serves the following benefits.
(i) According to the need of the shape, the job is marked by tools so that the correct amount of metal is removed to form the various shapes.
(ii) Drawing lines will serve as a guide indicating that a correct size has been achieved.
(it) No need to measure the job again and again.
(iv) Marked lines ensure the steps of operation.
(v) It also serves as the guidelines for the worker to perform the work.
(vi) Marking saves time.
Marking Media
A marking media is a substance, which is applied on the surface to be marked to distinguish the marked lines clearly. In other words, the material used for highlighting the marking lines on a job is called marking media.
Types of Marking Media/Marking Media Types
Whitewash
Prussian Blue
Copper Sulfate Cellulose Lacquer
Layout Die
Uses of Marking Media/Marking Media Uses
(i) Whitewash
Whitewash is used for painting the surface with white color on the job. Whitewash is prepared by
(a) chalk powder mixed with water.
(b) chalk mixed with methylated spirit.
(c) white lead powder mixed with turpentine.
It is used for rough, rusty, or mild steel jobs and not for finishing jobs.
Whitewash is not recommended for workpieces that have high accuracy. It is also not suitable for iron if it is prepared with water
(ii) Prussian Blue
This is used on filed or machine-finished surfaces. This will give very clear and accurate lines but takes more time to dry than the other marking media.
Prussian blue is a dye used in metalworking to aid in marking out rough parts for further machining. It is used to stain or paint a metal object with a very thin layer of dye that can be scratched off using a scriber or other sharp instrument to reveal a bright, yet very narrow line in the metal underneath. The advantages are that any existing scratches are covered with the dye and the new lines have a contrasting background. Moreover, the lines drawn are seen.
On rough structures, such as castings or forgings whitewash or a mixture of chalk and water can be used. A solution of copper sulfate, distilled water, and a few drops of sulfuric acid can be used on machined surfaces. This thin copper coating is more resistant to rough handling and the action of cutting fluid.
(iii) Copper Sulfate
This solution is prepared by mixing copper sulfate in water and a few drops of nitric acid. The copper sulfate is used on field or machine-finished surfaces. Copper sulfate sticks to the finished surfaces well.
Copper sulfate needs to be handled carefully as it is poisonous. Copper sulfate coating should be dried well Otherwise, the solution may stick on the instruments used for marking.
(iv) Cellulose Lacquer
This is a commercially available marking medium. It is available in different colors and dries very quickly.
(v) Layout Die
It is mostly used in 3D marking. It improves overall quality from design to production. It is an ink-type liquid, which is available in the market, in many colors. It is spread on the surface of the workpiece. It dries quickly and the marking is neat and clean. It is also used on surfaces.
Marking Methods
Centre Line Method
Marking by Template
Datum Line and Datum Surface
Centre Line Method
This method of marking is used on add-shaped jobs. An imaginary line is drawn in such types of job for marking and other lines are drawn on its basis.
Marking by Template
In this method, a template is used for marking which is made from a thin metal sheet according to sharp. This method is used for quick marking in mass production.
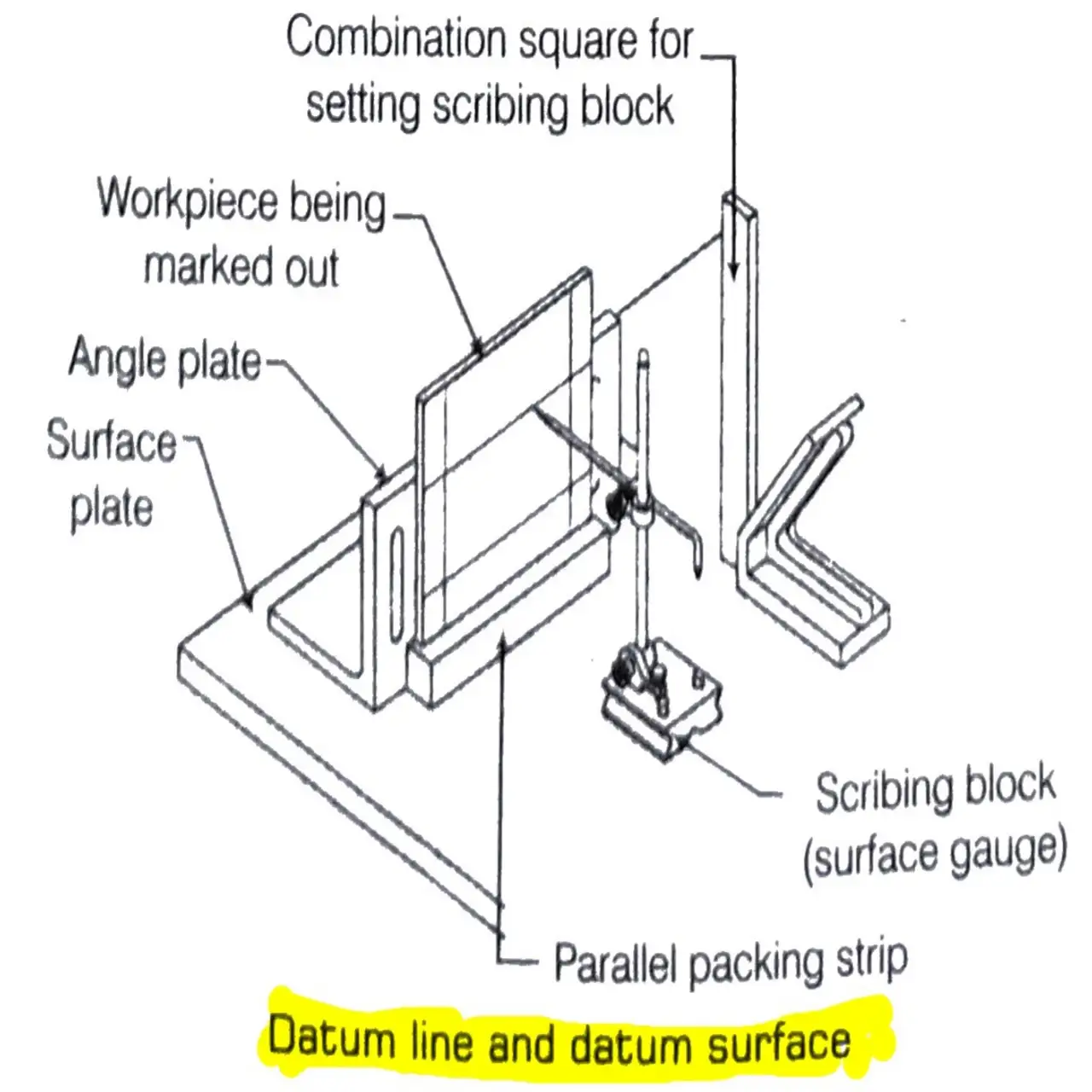
Datum Line and Datum Surface
The Datum line is a reference line from which all other lines are marked. This can be also a reference surface or plane for marking or measurement.
For most components, two datum lines are required, one horizontal and the other vertical, the intersecting point provides the common position.
The surface plate or marking table has a top surface that provides the datum surface. All measurements are done from this surface. All lines scribed by the scribing block or vernier height gauge will be parallel to this surface.
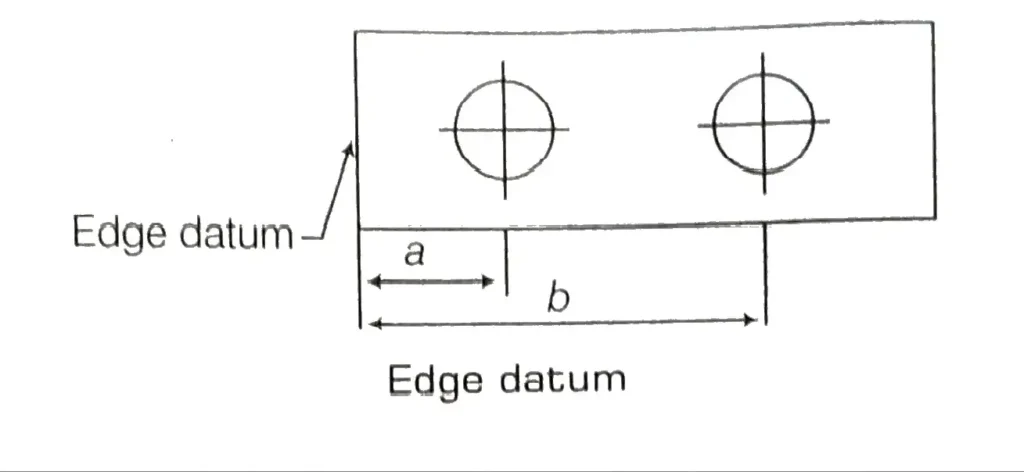
(i) Edge Datum
In this case, the datum surface is the edge of a work. All markings and measurements are carried out using the edge as the base.
(ii) Point Datum
In this case, the reference line is a point for marking and measurement.

(iii) Line Datum
This is a single line that you take dimensions from or along when you are measuring and marking out. The use of a center line as a datum is an example of a line datum.

Datum Line with Cumulative Error
When the marking is done progressively, as shown in Fig. (a), the maximum distance from the datum line AB to the 5th hole is 75.5 mm. The minimum distance from the datum line AB is 75.5 mm.
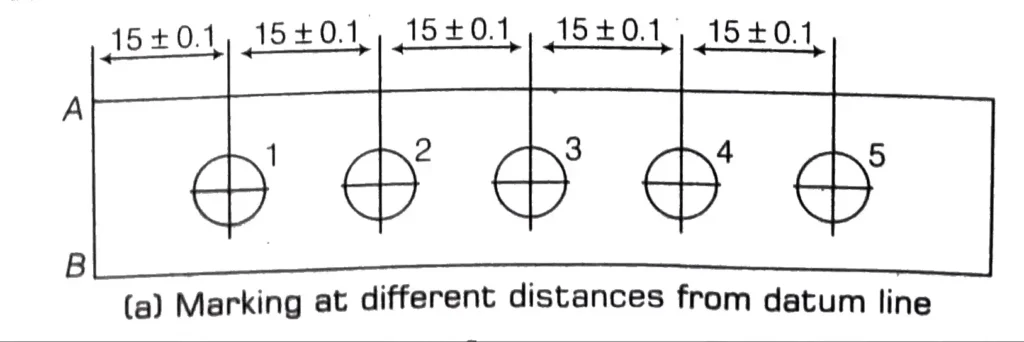
There is a tolerance of 1 mm in size. Assembly of matching parts and interchangeability may not be possible in such cases.
To avoid this error, each feature of the component should be marked out individually from the edge AB. (b). In this case, no hole will be more than the specified deviation of ± 0.1 mm and there is no possibility of build-up or cumulative error.
To avoid this error, each feature of the component should be marked out individually from the edge AB. (b). In this case, no hole will be more than the specified deviation of ± 0.1 mm and there is no possibility of build-up or cumulative error.

Purpose of Marking Related Precautions
Before starting the purpose of marking process, the following points must be remembered.
(i) Go through and understand the drawing before marking.
(ii) The reference point and reference line must be fixed.
(iii) The scriber must be pointed and hard so that the drawing is thin and clear.
(iv) Select the tools for marking according to the drawing and dimension.
(v) To ensure the lines, check the sign again.
(vi) The lines are drawn clearly by using a center punch.
(vii) At the time of drawing, the punch must be perpendicular to the surface